The use of underwater power cable for renewable energy has been proposed for a link from Morocco to UK, and another is for the SunCable link from Australia to Singapore. Why? Cheap renewable energy is in abundance in the sources, and the destination countries have a need to decarbonise and lower their energy costs. Overcomes the common complaint that the sun does not shine or the wind does not blow. But it does somewhere on Earth, and just have to connect the supply and demand. HVDC cables are used throughout the world (See Wikipedia). These 2 proposed links will be the longest and biggest globally.
Morocco to UK – XLINKS Project
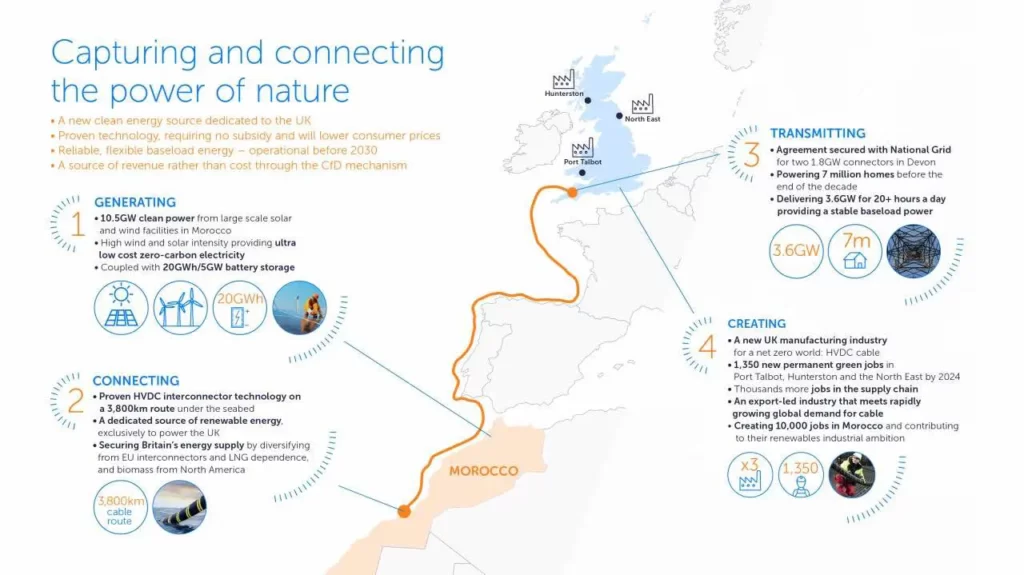
UK-based renewables company Xlinks is the project’s developer. Some details. Details will no doubt change over time.
- $21.9Billion cost
- Size = 10.5 gigawatt (GW) solar and wind farm
- Built in Morocco’s Guelmim-Oued Noun region
- 7 GW of solar and 3.5 GW of wind, along with onsite 20GWh/5GW battery storage,
- Four cables
- Twin 1.8 GW high voltage direct current (HVDC) subsea cables via 3800km (2,361miles) will be the world’s longest.
- Will cover an area of around 579 square miles (1,500 square kilometers) in Morocco
- Cables follow the shallow water route from Morocco to the UK, past Spain, Portugal, and France.
- Subsea cable manufacturer XLCC is going to build a factory in Hunterston, Scotland
- First phase between 2025-2027 connecting wind and solar power generated in Morocco to Alverdiscott, North Devon.
- Double the world’s current production of HVDC cable manufacturing, Need 90,000 metric tons of steel
- XLCC signed the UK Steel Charter at Parliament, in which it committed to using British steel.
- Xlinks will construct 7 GW of solar and 3.5 GW of wind, along with onsite 20GWh/5GW battery storage, in Morocco.
- First cable will be active in early 2027
- Further cables planned for 2029.
- The National Grid will provide two 1.8GW connections at Alverdiscott in Devon.
- Capable of powering a whopping 7 million UK homes by 2030.
- The project will be capable of supplying 8% of Britain’s electricity needs.
Update March 2024. Xlinks says that it contemplating taking the cable to Germany. (Bloomberg)
Sun Cable Australia to Singapore
Australia’s Northern Territory has abundant space and sun; Singapore is pressed for space, and looking to transition to renewable power, Sunconnect is said to be the world’s biggest clean energy project although the UK Morocco will be similar.
- US$22-billion infrastructure project (>$AU30b)
- 20GW Solar and Wind built
- Up to 3.2GW of energy through the cable
- 42GW Battery
- Transmission to Darwin via an 800MW overhead transmission line
- 4,200km (2,600 miles) to Singapore high voltage subsea cables. Some is in Australian waters (750km) and some in Indonesian
- Environmental studies are underway
- Capital raising close in 2023
- Deliver investment of more than $8 to Australia.
- Export revenue of $US2B
- 14,000 direct and indirect jobs, mostly in Australia.
- 1100 Australian jobs after construction
- Construction with selling power in Darwin by the start of 2027
- Singapore to come online at the start of 2029
- Provide up to 15 % of Singapore’s electricity and power all 1.37m households and more.
Status of Project June 2023
An endorsement by Infrastructure Australia, a government agency assisted the project in 2022 and allowed the project to advance.
The Singapore-based firm owners were the private firms of two of Australia’s richest people, Andrew Forrest’s Squadron Energy and Mike Cannon-Brookes’ Grok Ventures. MCB gained control of the venture in mid 2023. More to come.
Map of SunCable



Underwater power cable for renewable energy Technology
High voltage Direct Current (HVDC) is old technology and there are a number of HVDC systems. checkout Electrical for U site for more info. The massive transmission of electricity in the form of DC over long distances by means of submarine cables or overhead transmission has advantages with HVDC.
| HVDC | HVAC |
| Low losses. | Losses are high due to the skin effect and corona discharge |
| Better Voltage regulation and Control ability. | Voltage regulation and Control ability is low. |
| Transmit more power over a longer distance. | Transmit less power compared to a HVDC system. |
| Less insulation is needed. | More insulation is required. |
| Reliability is high. | Low Reliability. |
| Asynchronous interconnection is possible. | Asynchronous interconnection is not possible. |
| Reduced line cost due to fewer conductors. | Line cost is high. |
| Towers are cheaper, simple and narrow. | Towers are bigger compared to HVDC |
| Rectifiers at source, inverters as receiving end. | Transformers only |
Breakeven at 600-800 km










